그렇다면 HTTP 메시지 컨버터는 스프링 MVC 어디쯤에서 사용되는 것일까?
SpringMVC 구조
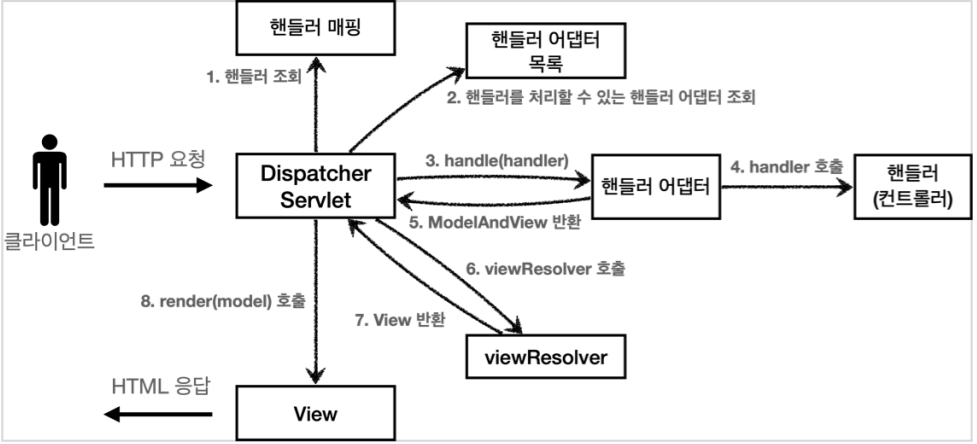
핵심은 애노테이션 기반의 컨트롤러, 그러니까 @RequestMapping 을 처리하는 핸들러 어댑터인
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter(요청 매핑 핸들러 어뎁터)에 있다.
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 동작 방식
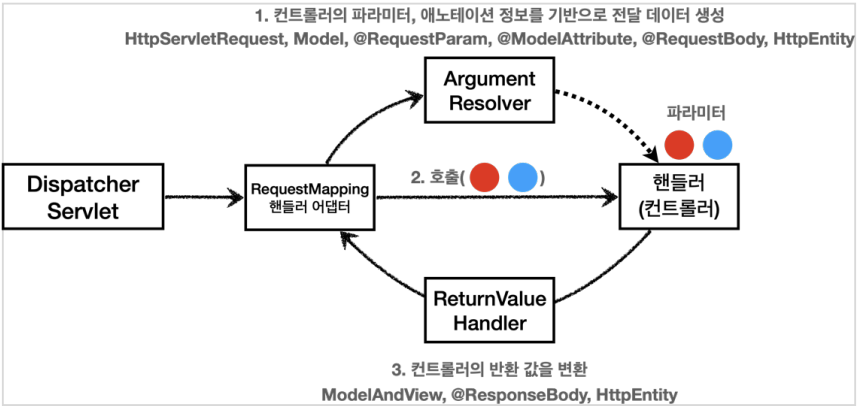
ArgumentResolver
생각해보면, 애노테이션 기반의 컨트롤러는 매우 다양한 파라미터를 사용할 수 있었다.
HttpServletRequest, Model은 물론이고, @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute 같은 애노테이션 그리고 @RequestBody, HttpEntity 같은 HTTP 메시지를 처리하는 부분까지 큰 유연함을 보여주었다.
이렇게 파라미터를 유연하게 처리할 수 있는 이유가 바로 ArgumentResolver 덕분이다.
애노테이션 기반 컨트롤러를 처리하는 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter는
바로 이 ArgumentResolver를 호출해서 컨트롤러(핸들러)가 필요로 하는 다양한 파라미터의 값(객체)을 생성한다.
그리고 이렇게 파라미터의 값이 모두 준비되면 컨트롤러를 호출하면서 값을 넘겨준다.
스프링은 30개가 넘는 ArgumentResolver를 기본으로 제공한다.
※ 참고
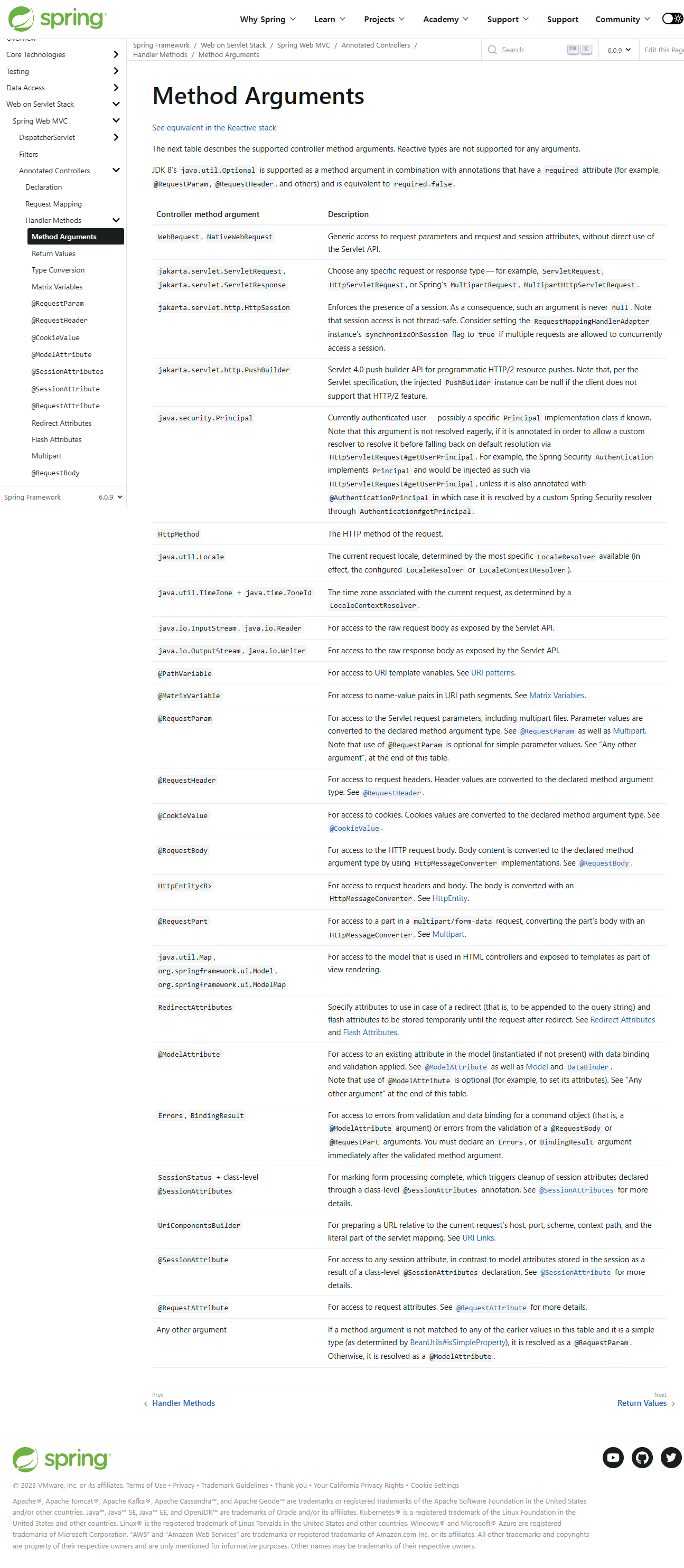
가능한 파라미터 목록은 다음 공식 메뉴얼에서 확인할 수 있다.
Method Arguments :: Spring Framework
Method Arguments :: Spring Framework
JDK 8’s java.util.Optional is supported as a method argument in combination with annotations that have a required attribute (for example, @RequestParam, @RequestHeader, and others) and is equivalent to required=false.
docs.spring.io
정확히는 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 인데 줄여서 ArgumentResolver 라고 부른다.
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
@Nullable
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
}
동작 방식
ArgumentResolver의 supportsParameter()를 호출해서 해당 파라미터를 지원하는지 체크하고,
지원하면 resolverArgument()를 호출해서 실제 객체를 생성한다.
그리고 이렇게 생성된 객체가 컨트롤러 호출 시 넘어가는 것이다.
그리고 직접 커스텀해서 인터페이스를 확장하여 원하는 ArgumentResolver를 만들 수도 있다.
ReturnVlueHandler
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler를 줄여서 ReturnValueHandler 라고 부른다.
ArgumentResolver와 비슷한데, 이것은 응답 값을 변환하고 처리한다.
컨트롤러에서 String으로 뷰 이름을 반환해도, 동작하는 이유가 바로 ReturnValueHandler 덕분이다.
스프링은 10여개가 넘는 ReturnValueHandler를 지원한다.
예) ModelAndView, @ResponseBody, HttpEntity, String
※ 참고
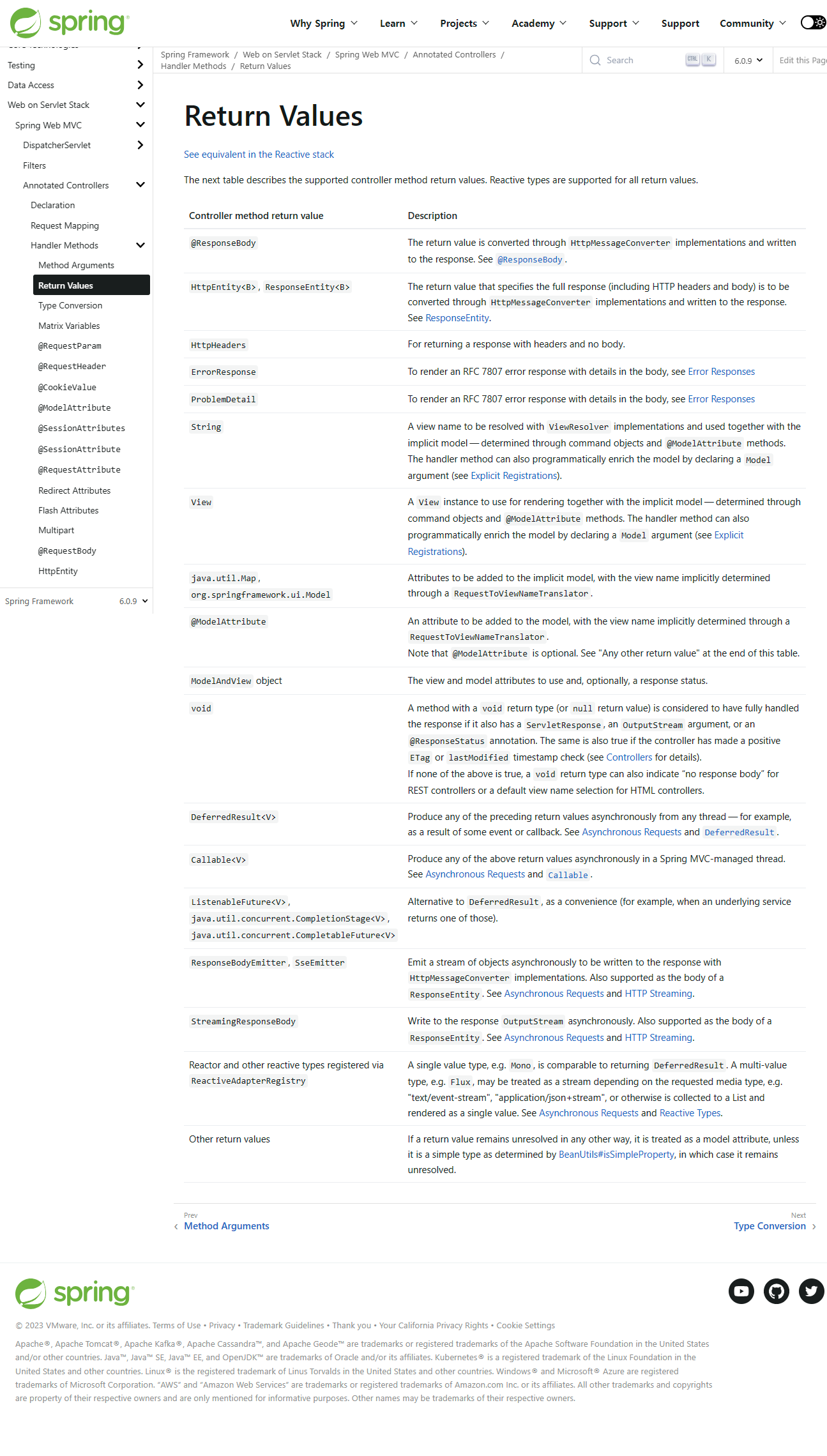
가능한 응답 값 목록은 다음 공식 메뉴얼에서 확인할 수 있다.
Return Values :: Spring Framework
Return Values :: Spring Framework
A single value type, e.g. Mono, is comparable to returning DeferredResult. A multi-value type, e.g. Flux, may be treated as a stream depending on the requested media type, e.g. "text/event-stream", "application/json+stream", or otherwise is collected to a
docs.spring.io
HTTP 메시지 컨버터
HTTP 메시지 컨버터 위치
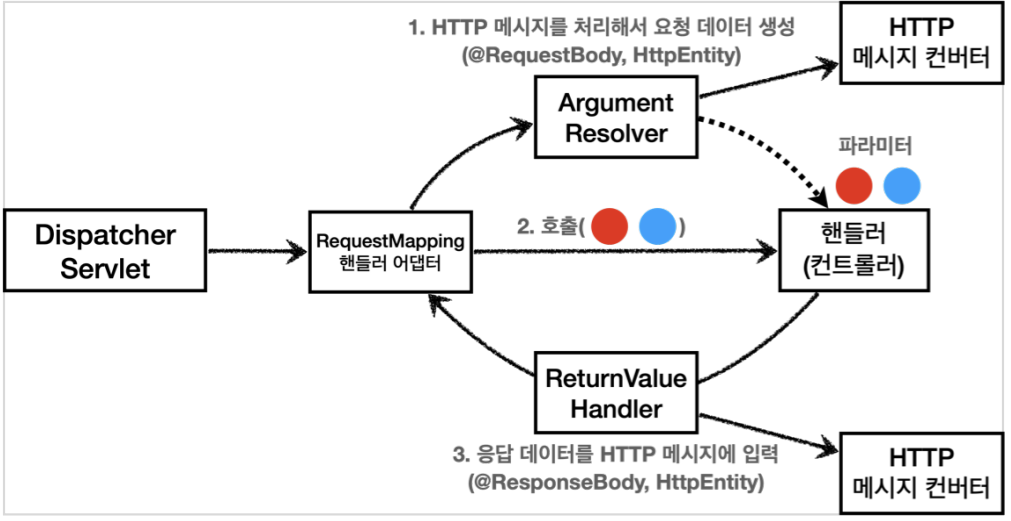
HTTP 메시지 컨버터는 어디쯤 위치해있을까?
HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 사용하는 @RequestBody도 컨트롤러가 필요로 하는 파라미터의 값에 사용된다.
@ResponseBody 의 경우도 컨트롤러의 반환 값을 이용한다.
요청의 경우 @RequestBody를 처리하는 ArgumentResolver가 있고, HttpEntity를 처리하는 ArgumentResolver가 있다.
이 ArgumentResolver들이 HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 사용해서 필요한 객체를 생성하는 것이다.
응답의 경우 @ResponseBody와 HttpEntity를 처리하는 ReturnValueHandler가 있다.
그리고 여기에서 HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 호출해서 응답 결과를 만든다.
스프링 MVC는 @RequestBody, @ResponseBody 가 있으면
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor(ArgumentResolver)
HttpEntity가 있으면 HttpEntityMethodProcessor(ArgumentResolver)를 사용한다,.
※ 참고
HttpMessageConverter
/*
* Copyright 2002-2021 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.http.converter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.HttpOutputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Strategy interface for converting from and to HTTP requests and responses.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 3.0
* @param <T> the converted object type
*/
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> {
/**
* Indicates whether the given class can be read by this converter.
* @param clazz the class to test for readability
* @param mediaType the media type to read (can be {@code null} if not specified);
* typically the value of a {@code Content-Type} header.
* @return {@code true} if readable; {@code false} otherwise
*/
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
/**
* Indicates whether the given class can be written by this converter.
* @param clazz the class to test for writability
* @param mediaType the media type to write (can be {@code null} if not specified);
* typically the value of an {@code Accept} header.
* @return {@code true} if writable; {@code false} otherwise
*/
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
/**
* Return the list of media types supported by this converter. The list may
* not apply to every possible target element type and calls to this method
* should typically be guarded via {@link #canWrite(Class, MediaType)
* canWrite(clazz, null}. The list may also exclude MIME types supported
* only for a specific class. Alternatively, use
* {@link #getSupportedMediaTypes(Class)} for a more precise list.
* @return the list of supported media types
*/
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
/**
* Return the list of media types supported by this converter for the given
* class. The list may differ from {@link #getSupportedMediaTypes()} if the
* converter does not support the given Class or if it supports it only for
* a subset of media types.
* @param clazz the type of class to check
* @return the list of media types supported for the given class
* @since 5.3.4
*/
default List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes(Class<?> clazz) {
return (canRead(clazz, null) || canWrite(clazz, null) ?
getSupportedMediaTypes() : Collections.emptyList());
}
/**
* Read an object of the given type from the given input message, and returns it.
* @param clazz the type of object to return. This type must have previously been passed to the
* {@link #canRead canRead} method of this interface, which must have returned {@code true}.
* @param inputMessage the HTTP input message to read from
* @return the converted object
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @throws HttpMessageNotReadableException in case of conversion errors
*/
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
/**
* Write a given object to the given output message.
* @param t the object to write to the output message. The type of this object must have previously been
* passed to the {@link #canWrite canWrite} method of this interface, which must have returned {@code true}.
* @param contentType the content type to use when writing. May be {@code null} to indicate that the
* default content type of the converter must be used. If not {@code null}, this media type must have
* previously been passed to the {@link #canWrite canWrite} method of this interface, which must have
* returned {@code true}.
* @param outputMessage the message to write to
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @throws HttpMessageNotWritableException in case of conversion errors
*/
void write(T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;
}
확장
스프링은 다음을 모두 인터페이스로 제공한다. 따라서 필요하면 언ㄴ제든지 기능을 확장할 수 있다.
1) HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
2) HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
3) HttpMessageConverter
스프링이 필요한 대부분의 기능을 제공하기 때문에 실제 기능을 확장할 일이 많지는 않다.
기능 확장은 WebMvcConfigurer 를 상속 받아서 스프링 빈으로 등록하면 된다.
WebMvcConfigurer
/*
* Copyright 2002-2021 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import org.springframework.format.Formatter;
import org.springframework.format.FormatterRegistry;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.validation.MessageCodesResolver;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter;
/**
* Defines callback methods to customize the Java-based configuration for
* Spring MVC enabled via {@code @EnableWebMvc}.
*
* <p>{@code @EnableWebMvc}-annotated configuration classes may implement
* this interface to be called back and given a chance to customize the
* default configuration.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Keith Donald
* @author David Syer
* @since 3.1
*/
public interface WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* Help with configuring {@link HandlerMapping} path matching options such as
* whether to use parsed {@code PathPatterns} or String pattern matching
* with {@code PathMatcher}, whether to match trailing slashes, and more.
* @since 4.0.3
* @see PathMatchConfigurer
*/
default void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure content negotiation options.
*/
default void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure asynchronous request handling options.
*/
default void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure a handler to delegate unhandled requests by forwarding to the
* Servlet container's "default" servlet. A common use case for this is when
* the {@link DispatcherServlet} is mapped to "/" thus overriding the
* Servlet container's default handling of static resources.
*/
default void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Add {@link Converter Converters} and {@link Formatter Formatters} in addition to the ones
* registered by default.
*/
default void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Add Spring MVC lifecycle interceptors for pre- and post-processing of
* controller method invocations and resource handler requests.
* Interceptors can be registered to apply to all requests or be limited
* to a subset of URL patterns.
*/
default void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Add handlers to serve static resources such as images, js, and, css
* files from specific locations under web application root, the classpath,
* and others.
* @see ResourceHandlerRegistry
*/
default void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Configure "global" cross-origin request processing. The configured CORS
* mappings apply to annotated controllers, functional endpoints, and static
* resources.
* <p>Annotated controllers can further declare more fine-grained config via
* {@link org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin @CrossOrigin}.
* In such cases "global" CORS configuration declared here is
* {@link org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration#combine(CorsConfiguration) combined}
* with local CORS configuration defined on a controller method.
* @since 4.2
* @see CorsRegistry
* @see CorsConfiguration#combine(CorsConfiguration)
*/
default void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Configure simple automated controllers pre-configured with the response
* status code and/or a view to render the response body. This is useful in
* cases where there is no need for custom controller logic -- e.g. render a
* home page, perform simple site URL redirects, return a 404 status with
* HTML content, a 204 with no content, and more.
* @see ViewControllerRegistry
*/
default void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Configure view resolvers to translate String-based view names returned from
* controllers into concrete {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.View}
* implementations to perform rendering with.
* @since 4.1
*/
default void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Add resolvers to support custom controller method argument types.
* <p>This does not override the built-in support for resolving handler
* method arguments. To customize the built-in support for argument
* resolution, configure {@link RequestMappingHandlerAdapter} directly.
* @param resolvers initially an empty list
*/
default void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers) {
}
/**
* Add handlers to support custom controller method return value types.
* <p>Using this option does not override the built-in support for handling
* return values. To customize the built-in support for handling return
* values, configure RequestMappingHandlerAdapter directly.
* @param handlers initially an empty list
*/
default void addReturnValueHandlers(List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers) {
}
/**
* Configure the {@link HttpMessageConverter HttpMessageConverter}s for
* reading from the request body and for writing to the response body.
* <p>By default, all built-in converters are configured as long as the
* corresponding 3rd party libraries such Jackson JSON, JAXB2, and others
* are present on the classpath.
* <p><strong>Note</strong> use of this method turns off default converter
* registration. Alternatively, use
* {@link #extendMessageConverters(java.util.List)} to modify that default
* list of converters.
* @param converters initially an empty list of converters
*/
default void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
}
/**
* Extend or modify the list of converters after it has been, either
* {@link #configureMessageConverters(List) configured} or initialized with
* a default list.
* <p>Note that the order of converter registration is important. Especially
* in cases where clients accept {@link org.springframework.http.MediaType#ALL}
* the converters configured earlier will be preferred.
* @param converters the list of configured converters to be extended
* @since 4.1.3
*/
default void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
}
/**
* Configure exception resolvers.
* <p>The given list starts out empty. If it is left empty, the framework
* configures a default set of resolvers, see
* {@link WebMvcConfigurationSupport#addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List, org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager)}.
* Or if any exception resolvers are added to the list, then the application
* effectively takes over and must provide, fully initialized, exception
* resolvers.
* <p>Alternatively you can use
* {@link #extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List)} which allows you to extend
* or modify the list of exception resolvers configured by default.
* @param resolvers initially an empty list
* @see #extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List)
* @see WebMvcConfigurationSupport#addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List, org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager)
*/
default void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
}
/**
* Extending or modify the list of exception resolvers configured by default.
* This can be useful for inserting a custom exception resolver without
* interfering with default ones.
* @param resolvers the list of configured resolvers to extend
* @since 4.3
* @see WebMvcConfigurationSupport#addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List, org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager)
*/
default void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
}
/**
* Provide a custom {@link Validator} instead of the one created by default.
* The default implementation, assuming JSR-303 is on the classpath, is:
* {@link org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.OptionalValidatorFactoryBean}.
* Leave the return value as {@code null} to keep the default.
*/
@Nullable
default Validator getValidator() {
return null;
}
/**
* Provide a custom {@link MessageCodesResolver} for building message codes
* from data binding and validation error codes. Leave the return value as
* {@code null} to keep the default.
*/
@Nullable
default MessageCodesResolver getMessageCodesResolver() {
return null;
}
}
'스프링 > 스프링 웹' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] 스프링 MVC - 상품 도메인 개발 및 상품 서비스 HTML - 부트스트랩 (0) | 2023.06.14 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] 스프링 MVC - 웹 페이지 만들기 프로젝트 생성, 요구사항 분 (0) | 2023.06.13 |
| [Spring] HTTP 메시지 컨버터 (0) | 2023.06.13 |
| [Spring] HTTP 응답 - HTTP API, 메시지 바디에 직접 입력 (1) | 2023.06.13 |
| [Spring] HTTP 응답 - 정적 리소스, 뷰 템플릿 (0) | 2023.06.12 |




댓글